?Hemoglobin
Each Red Blood Cell contains about 270 million Hemoglobin. So what is this magical Hemoglobin? Here we will look at the make up, function and diseases that make up the Hemoglobin.
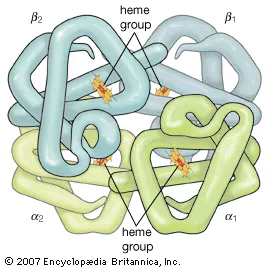
1/ Hemoglobin is made up of Heme and Globin. First we will look at the Heme then come back and look at the Globin. Here is the overall structure of Hemoglobin which is made up a iron (Fe2+), Protophorphyrin, and a group of 4 proteins called Globins.
2/ When we talk about the creation of the Heme group, you will hear the term heme synthesis. What this actually means is the long pathway of enzymes which are used to synthesize the Protoporphyrin IX molecule.

3/ The Protoporphyrin is actually a large chemical molecule which I think looks like a snowflake. It is made in a long process which involves several enzymes.
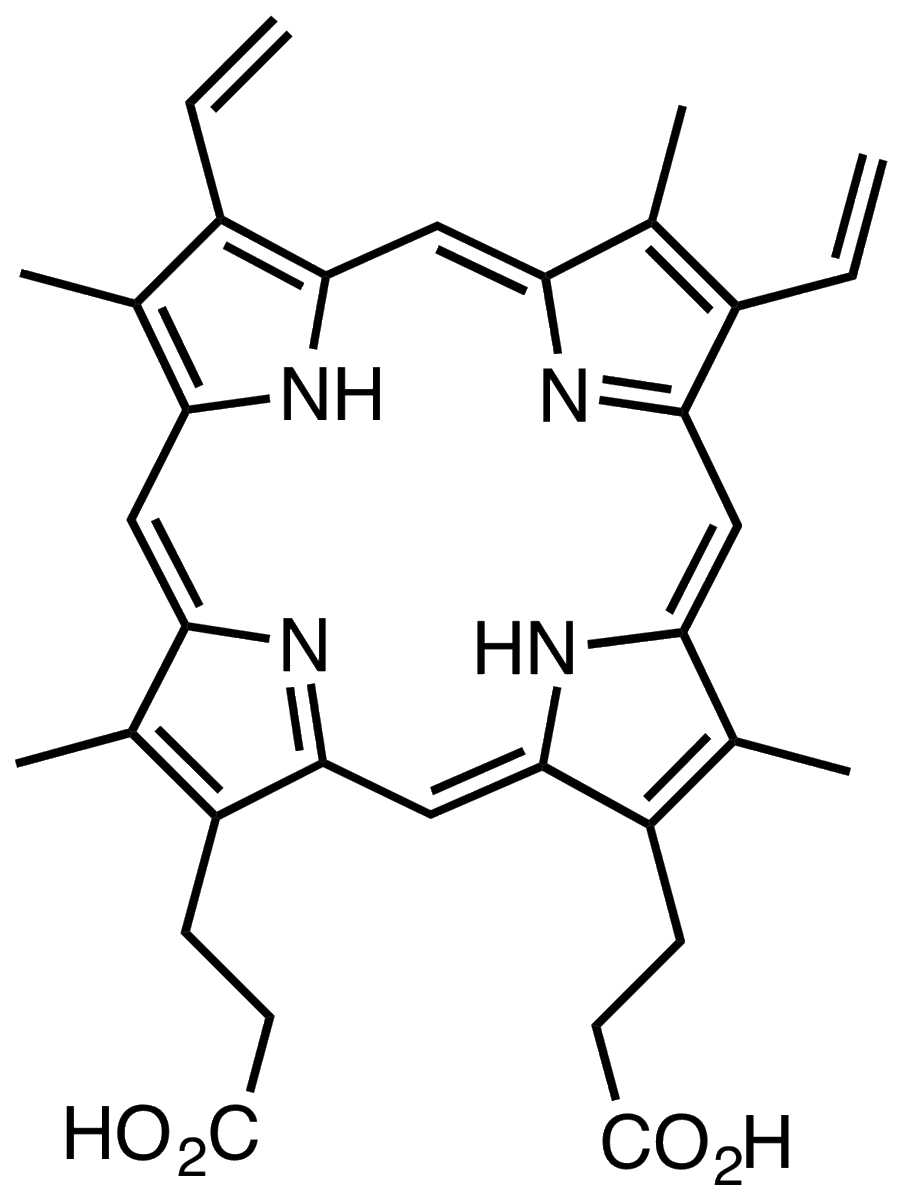
4/ Here comes our first set of diseases in Red Blood Cells. There is a group of disease called Porphyria that stem from defects in the enzymes which lead to a failure to make the protoporphyrin molecule. The intermediate steps of hem synthesis create intermediates that are toxic.
5/ When the next step fails due to a missing enzyme, the build up of these toxic intermediates occurs. This leads to Phorphyria. There are a few types of this disorder that attack the nerves and skin.
6/ Once the protoporphyrin is formed properly it will bind a single molecule of iron in the center. The only thing that can go wrong with iron is a lack of it. This is probably one of the largest anemias in the world. Iron Deficiency Anemia.
7/ A fully formed Heme group will contain 1 molecule of protoporphyrin and 1 molecule of iron. Next we have to look at the Globin proteins. The Globin is made up of 4 actual globin proteins which come together to form a 4 leaf clover like structure.
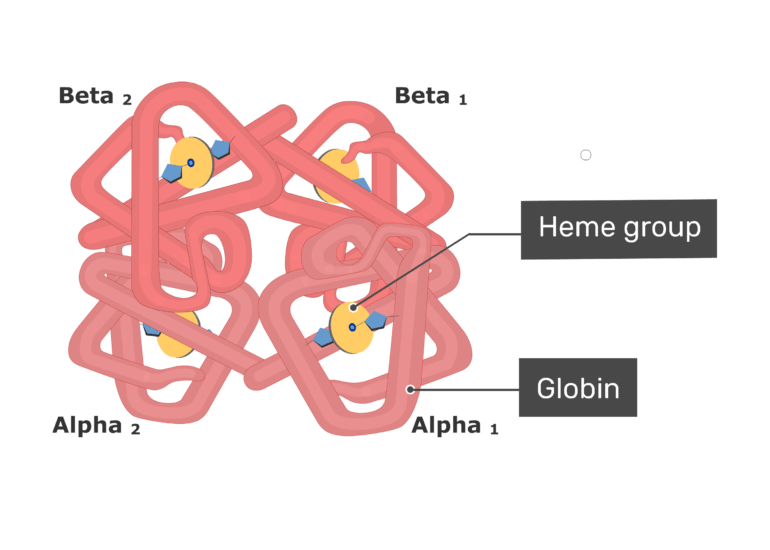
8/ Each of the Heme groups will bind in the center of one of the 4 Globin proteins to complete the Hemoglobin. Now we need to look at these 4 globin proteins as they are not always the same and their are a few diseases that stem from them.
9/ When the Embryo is in early development, the Red Blood Cells will make Hemoglobin with 2 Zeta and 2 Epsilon globin proteins. This is called Embryonic Hemoglobin (HbE)
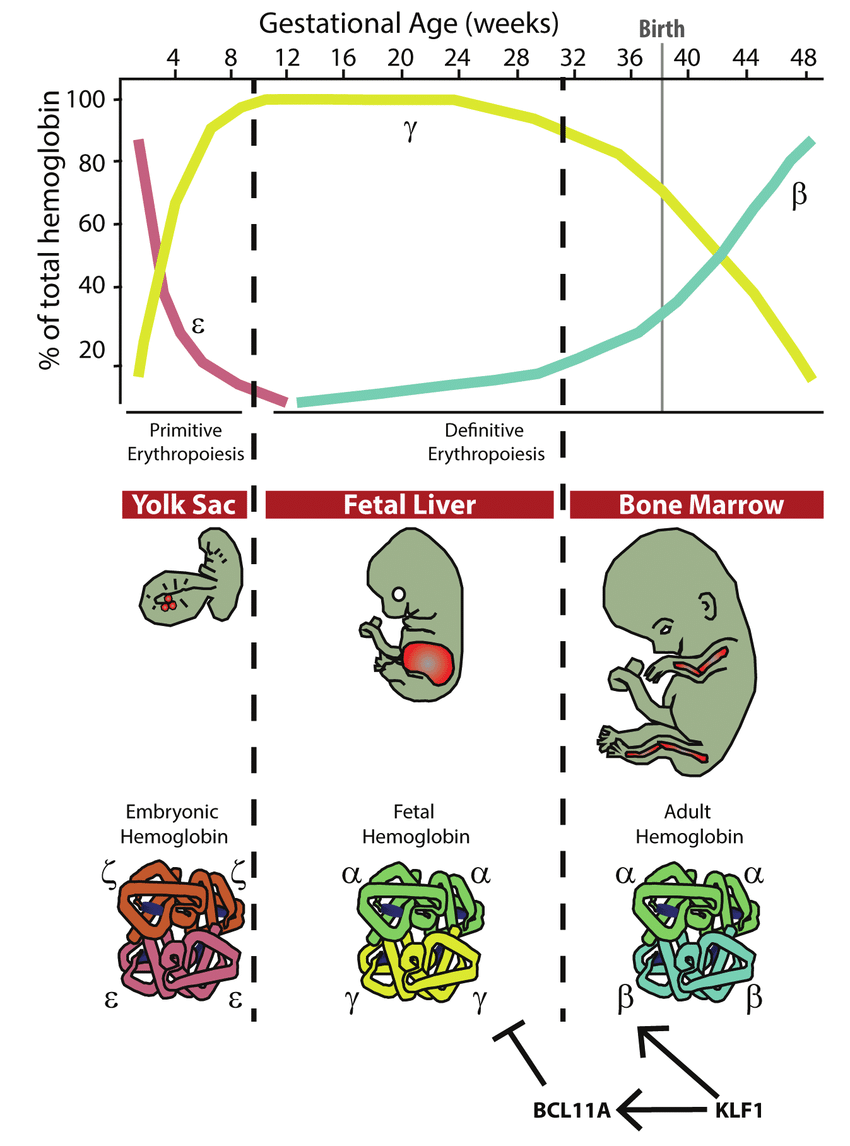
10/As the baby develops into a fetus, it will begin to produce hemoglobin using 2 Alpha and 2 Gamma globin. This will be called Fetal Hemoglobin (HbF). The famous gene BCL11A regulates the transfer from Fetal Hb to Adult Hb.
10/ From the time the baby is born until about 2 years of age, the process of transfer from Fetal to Adult Hb will take place. There are actually 2 kinds of Adult Hb. The first is the common hemoglobin which takes 2 alpha and 2 beta globin proteins. This is called HbA1.
11/ The other is another adult Hb that is made up 2 alpha and 2 delta globin proteins. This is called Adult Hb type 2 or HbA2. The blood consists of about 95% to 98% Adult HbA1 and 1% to 3% Adult HbA2. In the average adult Fetal Hb will be made at less than 1%.
12/ The first disease from Globin genes comes from the Alpha globin. There are 4 genes for these proteins. You get 2 from mom and 2 from dad. Depending on how many of the 4 genes are lost will determine what level of Alpha Thalassemia the patient will have.
13/ The next disease comes from the Beta Globin genes. There are only 2 of these genes. You get 1 from mom and 1 from dad. These mutations can vary in the level of Beta globin that is produced from the full amount to absolutely none.
14/ Patients with both genes making no beta globin are the most severe form of Beta Thalassemia. This is often called Beta Thalassemia major.
15/ The last disease comes from a single point mutation in the Beta Globin. This results in a fully functional Beta Globin under most conditions. This leads to a disease called Sickle Cell Anemia.
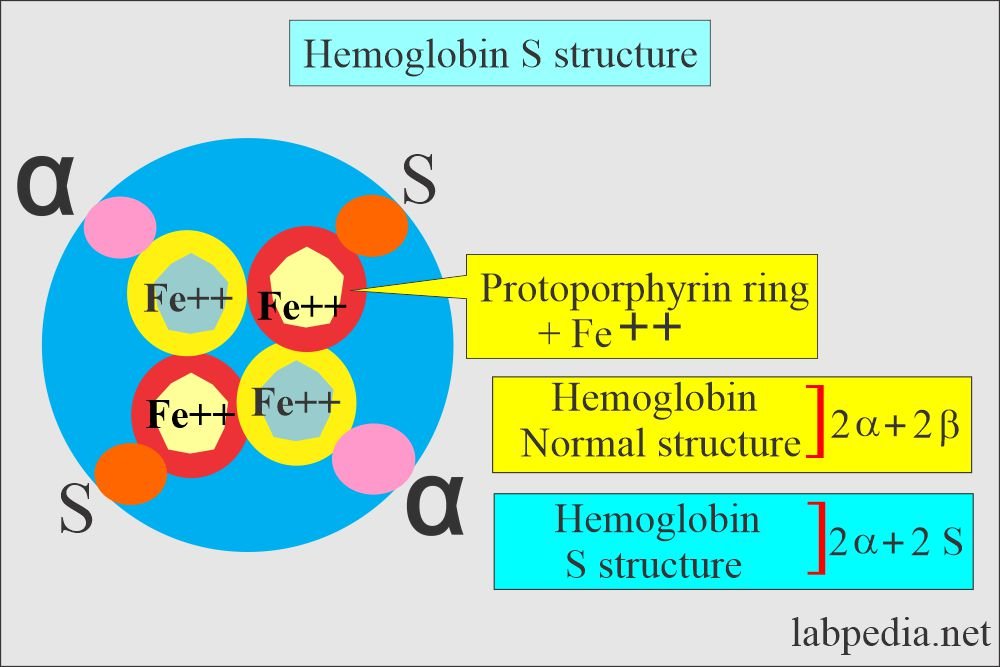
16/ These mutated forms of Hemoglobin Beta are named Hemoglobin S (HbS) for Sickling. This single point mutation causes the hemoglobin to bind together into long chains when the oxygen level gets to low.
17/ This polymerization of the HbS causes the Red Blood Cell to take on a Boomerang shape. These sickle shaped Red Blood Cells can block vessels and cause potentially life threatening blockages.
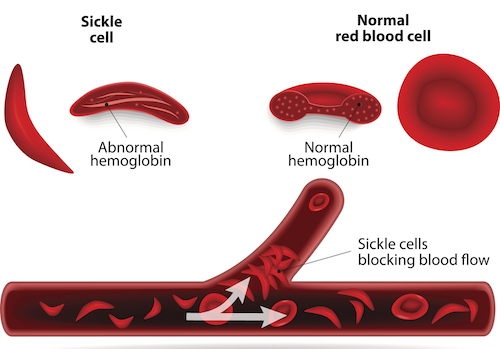
18/ This can lead to intense pain and even more serious events like a heart attack, pulmonary embolism or stroke. These odd shaped cells will often get destroyed in the spleen which leads to anemia.
19/ Next we will look at the tests of the blood that will inform us about the health of Red Blood cells.