Time for a deep dive into SARS-CoV-2 immunology after vaccination and infection. I’ll try to explain it also for non immunologists. New observation: Booster mRNA vaccines induce antibody switch to IgG4, what does this mean? https://t.co/dV1iYeHxaA https://t.co/f4RZSzPYh8 1/
science.org/doi/epdf/10.11…
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36548397/

It is known that immune responses could either protect against disease or exacerbate disease. Early non-neutralizing, afucosylated IgG1 antibody responses are associated with COVID-19 severity. https://t.co/LMpos8ZGIW https://t.co/Q4S5vIAZgi 2/
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35040666/
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36385627/
Previously it was shown that the afucosylated IgG1 antibodies are only found after the first vaccination. https://t.co/5SWEpbryX0 https://t.co/pbCCgrvvGs 3/
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…
ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/P…
Evidence for enhanced efficacy of afucosylated therapeutic IgG1 in vivo in antibody dependent cellular cytotoxicity by macrophages or neutrophils. https://t.co/2Q0BqhN1vD 4/
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35844552/
IgG4? B-cells make antibodies and during affinity maturation the type of antibodies changes – it matures too. Different antibodies have different functions. It starts of with IgM (coded by μ) and then switches with stronger binding antibodies to IgG1-IgG4 (γ1- 5/
IgA1 (α1), IgA2 (α2), and IgE (ε). The IgAs are mucosal antibodies that could protect from infections, IgE is known from type 1 (acute) allergy, but what is the difference between those different forms of IgG? That raises some questions on the role of IgG4 in COVID-19. 6/
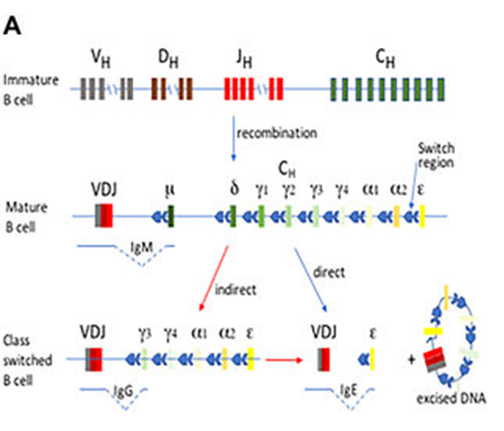
The authors note a reduced capacity of the spike-specific antibodies to mediate antibody-dependent cellular phagocytosis (by neutrophils) and complement deposition. #neutrophils will be less activated by IgG4 antibodies. 7/
IgG4 reduces exacerbations of immune reactions e.g., by IgE, and thus unwanted immune responses. IgG4 might be predicted to have similar effects than dexamethasone that saves lives of patients at the ICU. https://t.co/4qq39uzNU0 8/
researchgate.net/publication/32…

Is less neutrophil activation a good or a bad thing for immunity against COVID-19? Another study shows that the activation of myelopoietic responses #neutrophils is associated with disease severity. https://t.co/ucEthDnjOb 9/
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36208629/

The switch to IgG4 would fit with the contradictory results seen after the fourth vaccine dose. The 4th booster increased antibody titers but less than earlier boosters, yet was effective in reducing the rate and severity of disease. https://t.co/Rsu4MmSa61 10/12
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36367927/

Thus, the immune response seems to become less harmful for the person and more effective against the virus with subsequent vaccinations and class switching from IgG1 to IgG4 might be part of this. 11/12
The route in immune maturation after repeated mRNA vaccination would be IgM -> IgG1 afucosylated -> IgG1 fucosylated -> IgG4 with -less activation of neutrophils -Less severe disease However this does occur after infection & other vaccines. 12/12
The route in immune maturation after repeated mRNA vaccination would be IgM -> IgG1 afucosylated -> IgG1 fucosylated -> IgG4 with -less activation of neutrophils -Less severe disease However this does NOT occur after infection & other vaccines.
@UnrollThread
@johnjljacobs @UnrollThread Thank you, this thread was very helpful :)
@UrmelMurmel2022 @UnrollThread You're welcome.
@johnjljacobs @UnrollThread are you saying that the first booster is good, but, a second one is even better ?
@UnrollThread Updates to my 🧵 afucosylated IgG promotes inflammation by lung macrophages https://t.co/Jlnvlfvwrw And is a prothrombotic stimulus for platelets https://t.co/4T3uei3HKR https://t.co/wp8ckrOl0r
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33979301/
pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34315173/
unrollthread.com/t/160637570838…
